Accounting rate of return (also known as simple rate of return) is the ratio of estimated accounting profit of a project to the average investment made in the project. The accounting rate of return, also known as the return on investment, gives the annual accounting profits arising from an investment as a percentage of the investment made. The Accounting Rate of Return (ARR) provides firms with a straight-forward way to evaluate an investment’s profitability over time. A firm understanding of ARR is critical for financial decision-makers as it demonstrates the potential return on investment and is instrumental in strategic planning. Investment evaluation, capital budgeting, and financial analysis are all areas where ARR has a strong foundation.
- Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications.
- It is a useful tool for evaluating financial performance, as well as personal finance.
- Find out everything you need to know about the Accounting Rate of Return formula and how to calculate ARR, right here.
- For a project to have a good ARR, then it must be greater than or equal to the required rate of return.
- The accounting rate of return is a capital budgeting metric to calculate an investment’s profitability.
Define (RoR) in Simple Terms
Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise. Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs. Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications. Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others.
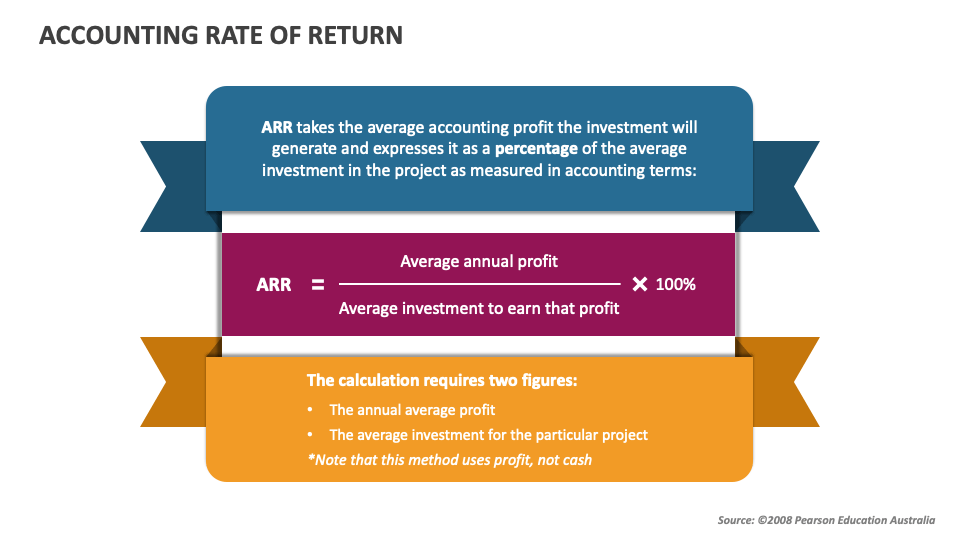
Accounting Rate of Return
The initial investment required to be made for this new project is 200,000. Based on this information, you are required to calculate the accounting rate of return. The Accounting Rate of Return formula is straight-forward, making it easily accessible for all finance professionals. It is computed simply by dividing the average annual profit gained from an investment by the initial cost of the investment and expressing the result in percentage.
What Is the Accounting Rate of Return Useful For?
Ask a question about your financial situation providing as much detail as possible. Our goal is to deliver the most understandable and comprehensive explanations of financial topics using simple writing complemented by helpful graphics and animation videos. We follow strict ethical journalism practices, which includes presenting unbiased information and citing reliable, attributed resources. At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content.
Accounting Rate of Return (ARR) is a formula used to calculate the net income expected from an investment or asset compared to the initial cost of investment. Company ABC is planning to purchase new production equipment which cost $ 10M. The company expects to increase the revenue of $ 3M per year from this equipment, it also increases the operating expense of around $ 500,000 per year (exclude depreciation). However, the formula doesn’t take the cash flow of a project or investment into account. It should therefore always be used alongside other metrics to get a more rounded and accurate picture.
Of course, that doesn’t mean too much on its own, so here’s how to put that into practice and actually work out the profitability of your investments. Next we need to convert this profit for the whole project into an average figure, so dividing by five years gives us $8,000 ($40,000/5). Candidates should note that accounting rate of return can not only be examined within the FFM syllabus, but also the F9 syllabus. Note that the value of investment assets at the end of 5th year (i.e. $50m) is the sum of scrap value ($10 m) and working capital ($40 m).
It offers a solid way of measuring financial performance for different projects and investments. Any asset that has a cost to purchase and will produce income at some point in the future, from selling or otherwise, has a calculable rate of return. Simple rate of return is sometimes called the basic growth rate or return on investment. The rate of return, or RoR, is the net gain or loss on an investment over a period of time. Generally, the higher the average rate of return, the more profitable it is. However, in the general sense, what would constitute a “good” rate of return varies between investors, may differ according to individual circumstances, and may also differ according to investment goals.
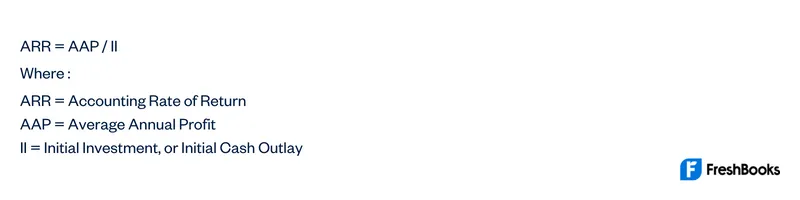
The accounting rate of return is a capital budgeting indicator that may be used to swiftly and easily determine the profitability of a project. Businesses generally utilize ARR to compare several projects and ascertain the expected rate of return for each one. As well as to assist in making acquisition or average investment decisions. As we can see from this, the accounting rate of return, unlike investment appraisal methods such as net present value, considers profits, not cash flows.
Its adaptability makes it useful for a wide range of applications, including assessing the economic profitability of projects, benchmarking performance, and improving resource allocation. The ARR is the annual percentage return from an investment based on its initial outlay. The required rate of return (RRR), accountant the or the hurdle rate, is the minimum return an investor would accept for an investment or project that compensates them for a given level of risk. It is calculated using the dividend discount model, which accounts for stock price changes, or the capital asset pricing model, which compares returns to the market.
The ARR formula calculates the return or ratio that may be anticipated during the lifespan of a project or asset by dividing the asset’s average income by the company’s initial expenditure. The present value of money and cash flows, which are often crucial components of sustaining a firm, are not taken into account by ARR. The accounting rate of return (ARR) formula divides an asset’s average revenue by the company’s initial investment to derive the ratio or return generated from the net income of the proposed capital investment.
Further management uses a guideline such as if the accounting rate of return is more significant than their required quality, then the project might be accepted else not. The RRR can vary between investors as they each have a different tolerance for risk. For example, a risk-averse investor requires a higher rate of return to compensate for any risk from the investment. Investors and businesses may use multiple financial metrics like ARR and RRR to determine if an investment would be worthwhile based on risk tolerance. The time value of money is the main concept of the discounted cash flow model, which better determines the value of an investment as it seeks to determine the present value of future cash flows.
